Ueno Royal Museum

The "Five Great Ukiyo-e Artists – Utamaro, Sharaku, Hokusai, Hiroshige, Kuniyoshi" exhibition , which brings together masterpieces by the five biggest stars of the golden age of ukiyo-e, has opened at the Ueno Royal Museum (Ueno, Tokyo). The exhibition will run until Sunday, July 6, 2025.
At the gallery talk held prior to the press preview, Noriko Yamamoto, curator at the Kawasaki Ukiyo-e Gallery and author of the exhibition catalogue, took to the stage. She explained the highlights of the exhibition, which we will introduce below along with a look at the exhibition.

Five artists who made their name with ukiyo-e, Japan's most popular art form that reached its golden age during the Tenmei and Kansei periods, are Kitagawa Utamaro, Toshusai Sharaku, Katsushika Hokusai, Utagawa Hiroshige, and Utagawa Kuniyoshi . This exhibition will display around 140 pieces, focusing on their masterpieces, which reached the pinnacle of their respective fields, such as portraits of beautiful women, actors, and landscapes, and will convey the distinctive features and appeal of their artistic expression.
Chapter 1: Kitagawa Utamaro: Thoughtful Women
The exhibition is divided into five chapters, each focusing on one artist, and the first to appear is Kitagawa Utamaro .
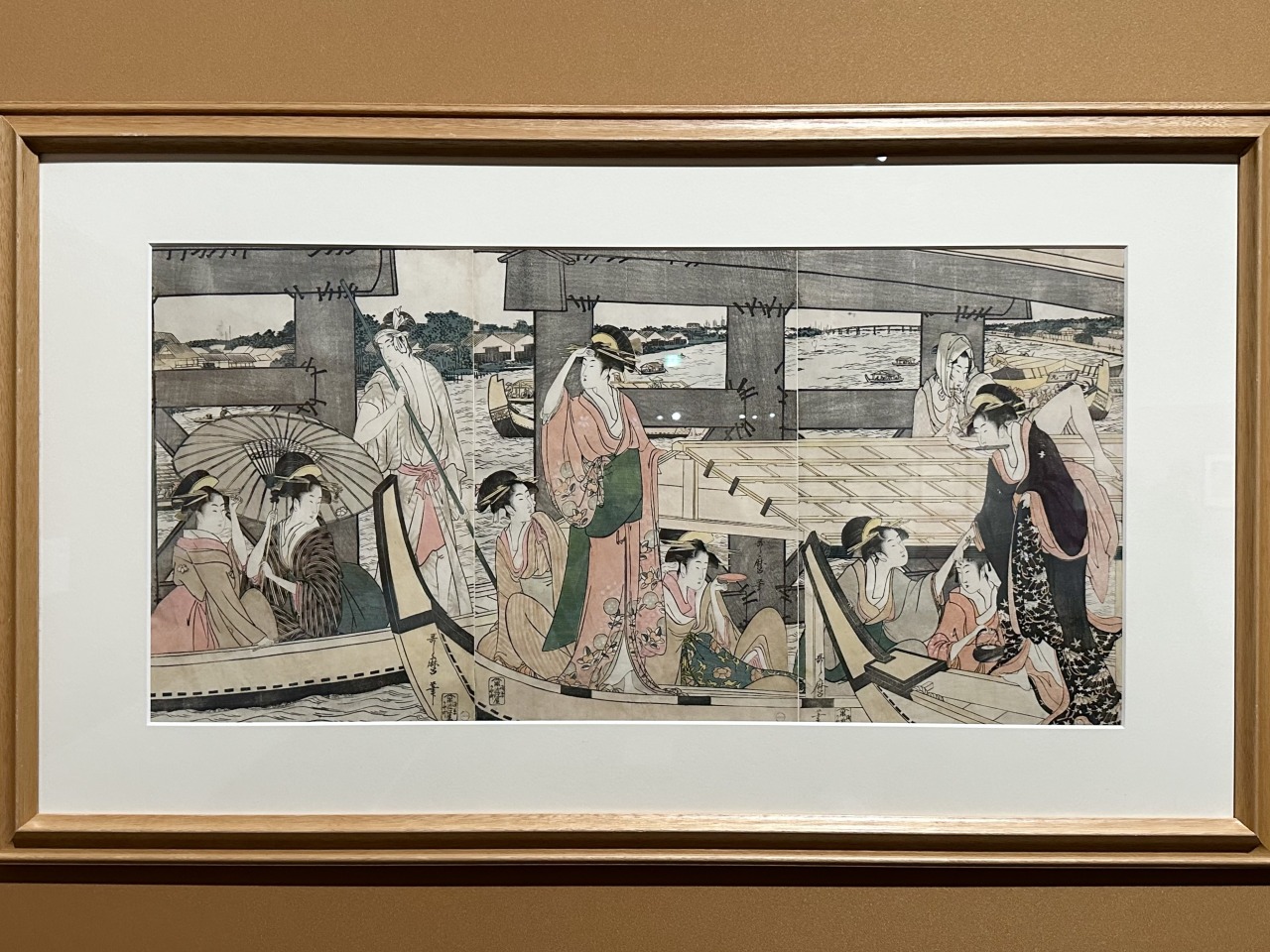

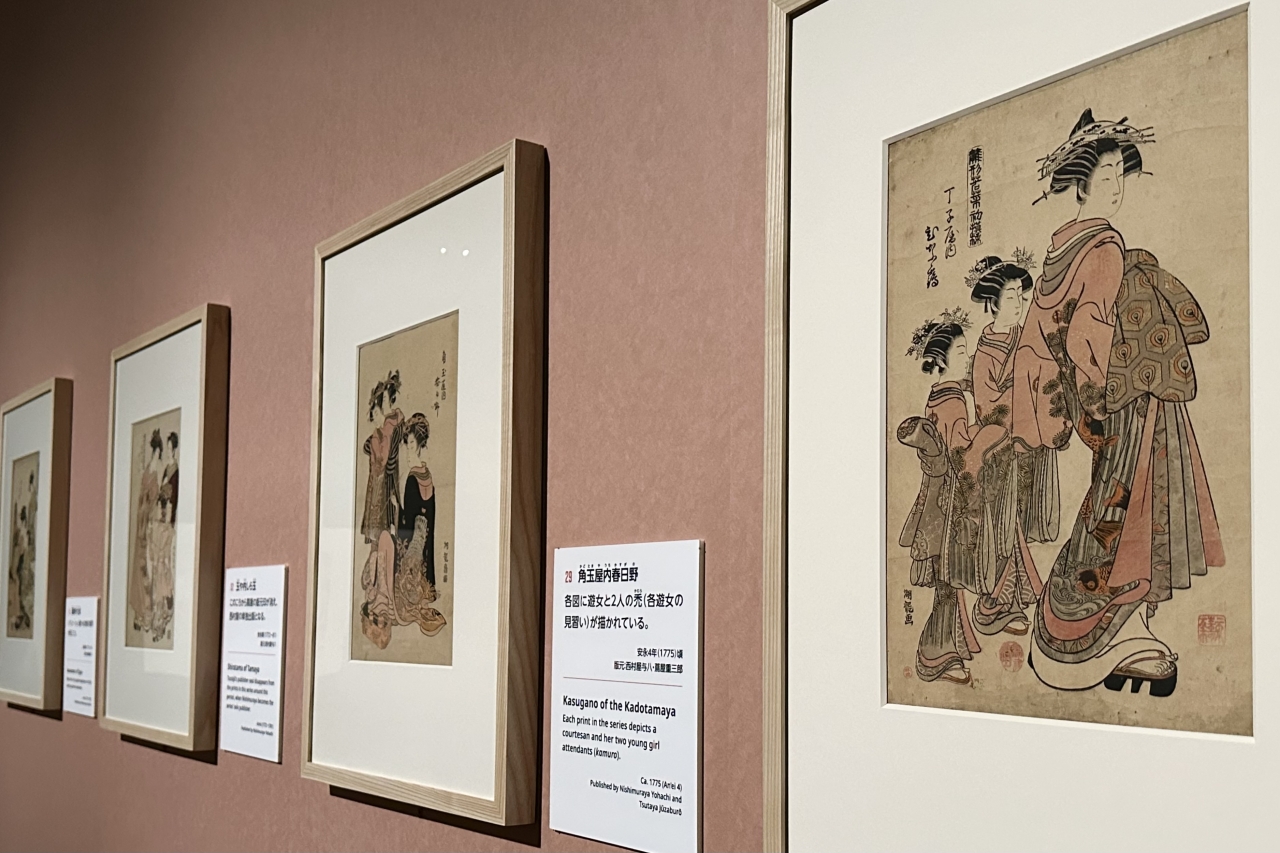
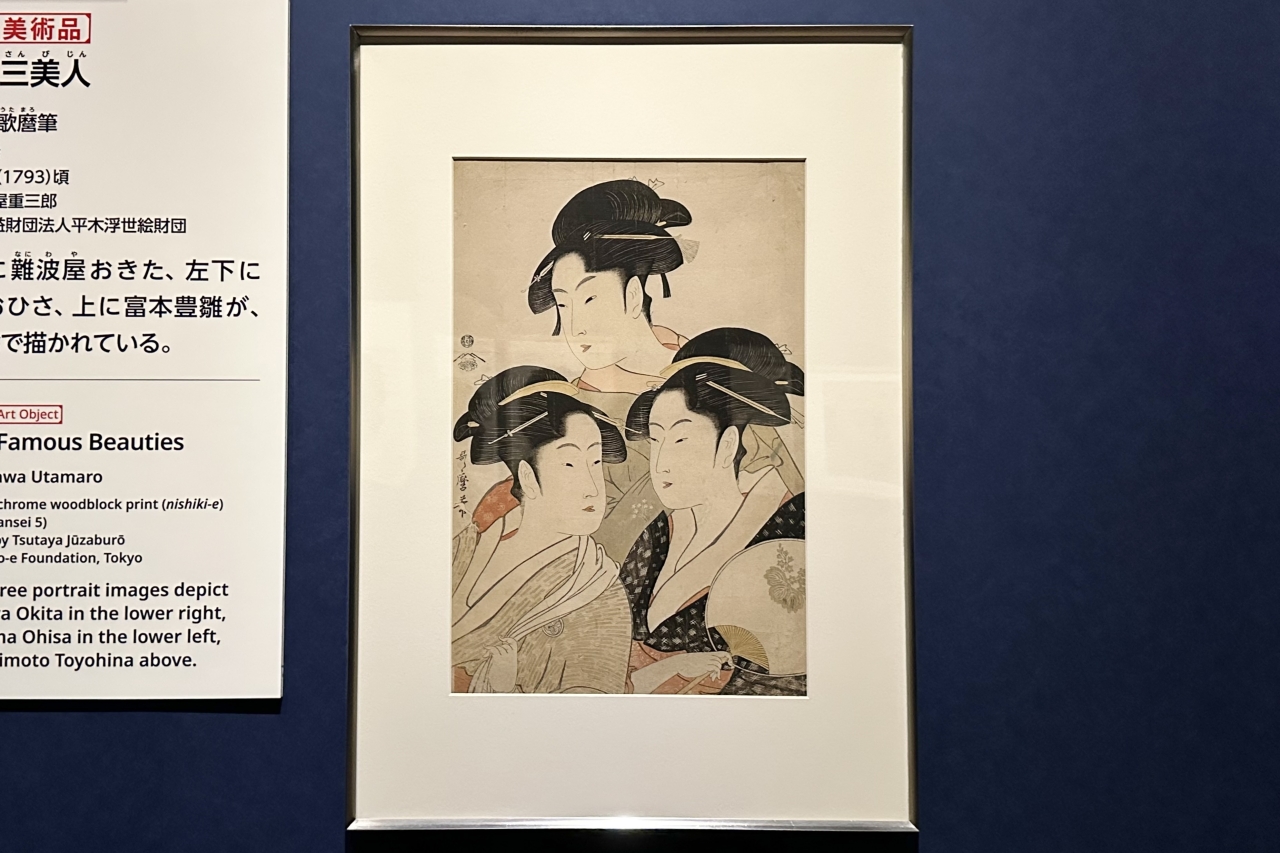
Utamaro is known as an artist who was discovered by Edo's most famous producer, Tsutaju (Tsutaya Jusaburo), who is also active in the historical drama "Berabou – Tsutaju Eika no Yumebanashi" currently being broadcast on NHK.
He teamed up with Tsutaju and introduced the "Okubi-e" style, which featured a close-up of the upper body of a person, a style that was used in paintings of actors at the time, to the painting of beautiful women. He became a leading figure in the painting of beautiful women, and took the world by storm with his works that depicted the graceful gestures and thoughts of women.

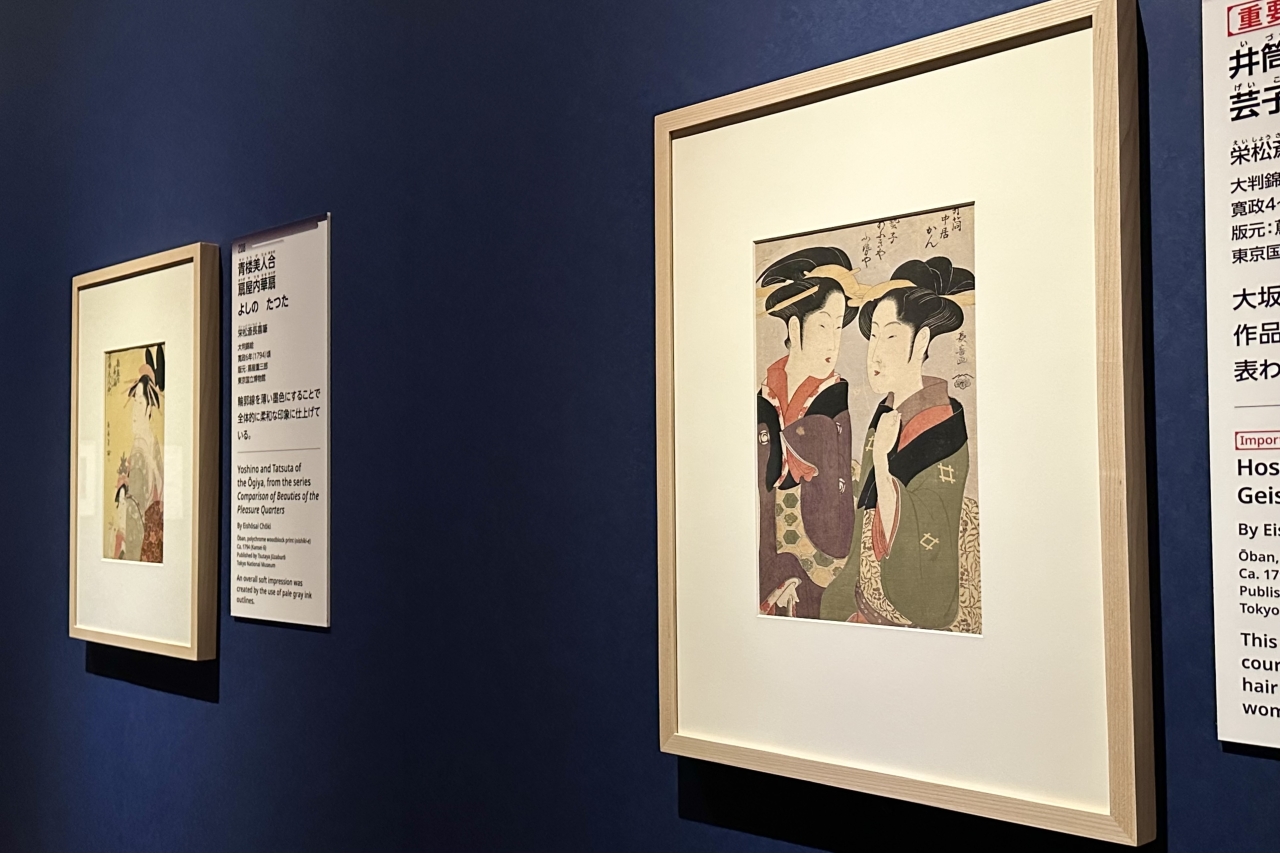
The exhibition focuses on portraits of beautiful women depicting everyday scenes, such as Five Beauties Competing for Charm: The Flower Wife of Hyogoya, which depicts a courtesan with disheveled hair reading a letter, rather than a woman dressed in elegant attire.
In the "Lessons for Parents" series, which contains morals for women, a "bakuren" (a carefree woman) appears, dressed in sloppy clothes and sipping alcohol. Bijin-ga (portraits of beautiful women) tend to depict the beauties of the time, such as the intelligent and beautiful courtesans who were the object of common people's admiration, or the popular poster girls of the town, but Utamaro, in a sense, used women with the polar opposite attributes as his models without distinction.
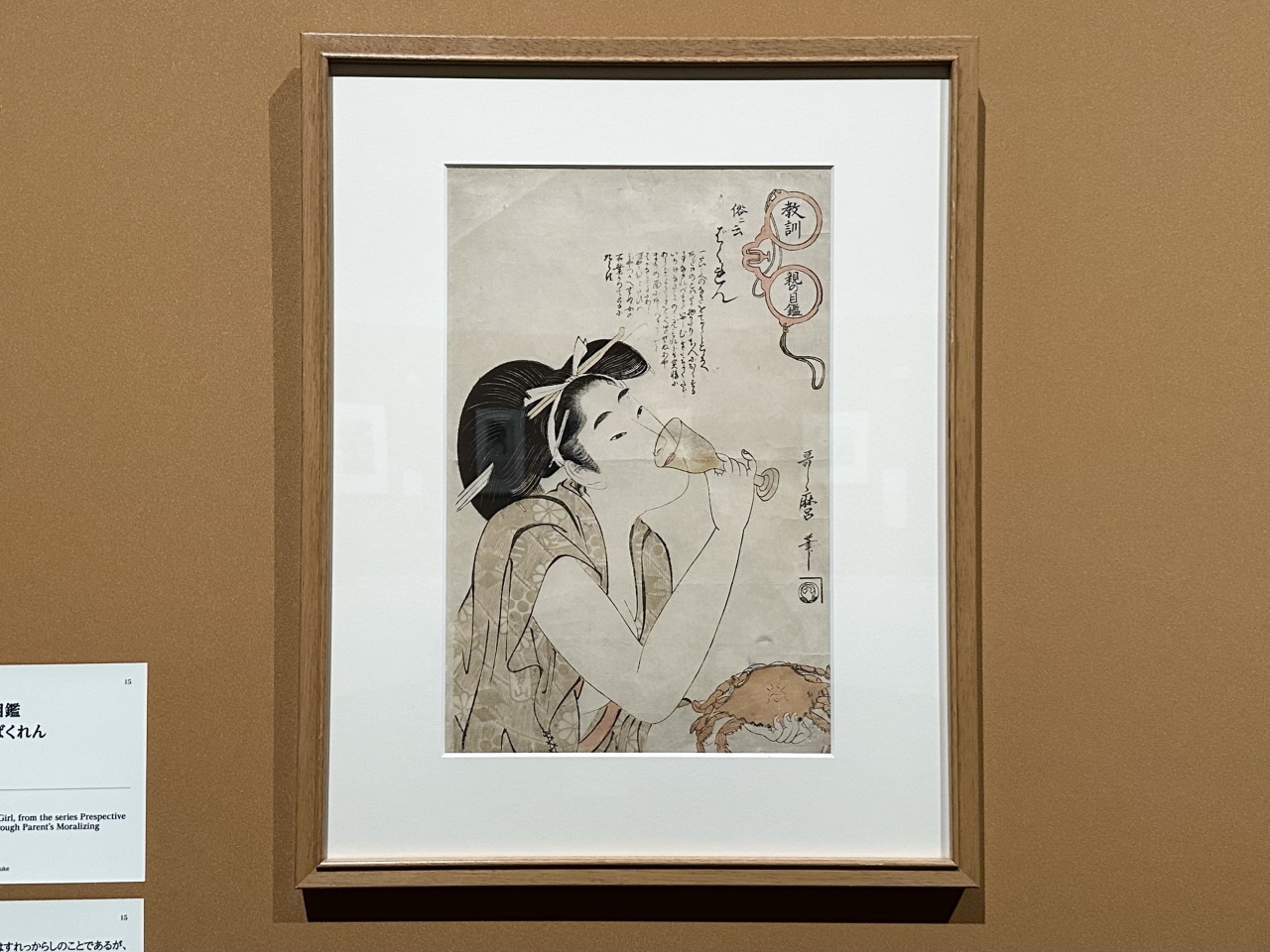

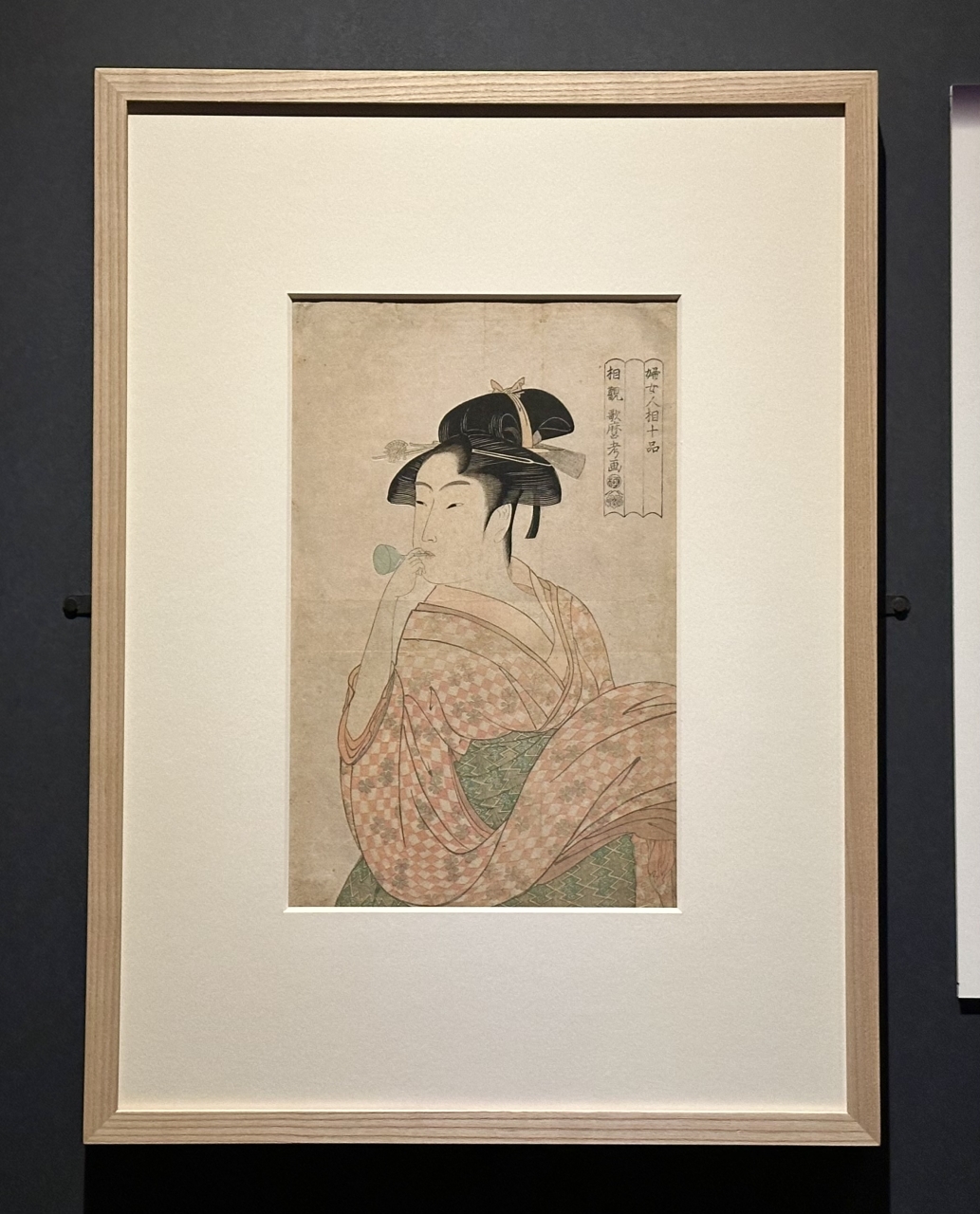
Yamamoto commented, "Utamaro's portraits of beautiful women are often depicted as ideal images of women, but he was actually also good at depicting these villainous women."
Utamaro was interested in the lifestyles and customs of women of all kinds, and used them as his subject matter, covering them all: an older sister watching over her younger brother playing at home with a smile, a female diver resting on the beach, a mountain witch nursing her child, etc. He said that a major feature of Utamaro's work is that he presents the charms of such diverse women with a rich expressiveness that allows us to imagine the story behind them, right down to the tip of a finger.

By the way, in the letter illustrated in the aforementioned "Five Beauties Competing for Love, the Flower Wife of Hyogoya," there is a sentence that begins with "I hate to imitate, I don't copy, I am a self-made artist," which gives a glimpse of Utamaro's firm pride as a painter of beautiful women. If you can read cursive writing, please take a look.
Chapter 2: Toshusai Sharaku – The impact of actor paintings
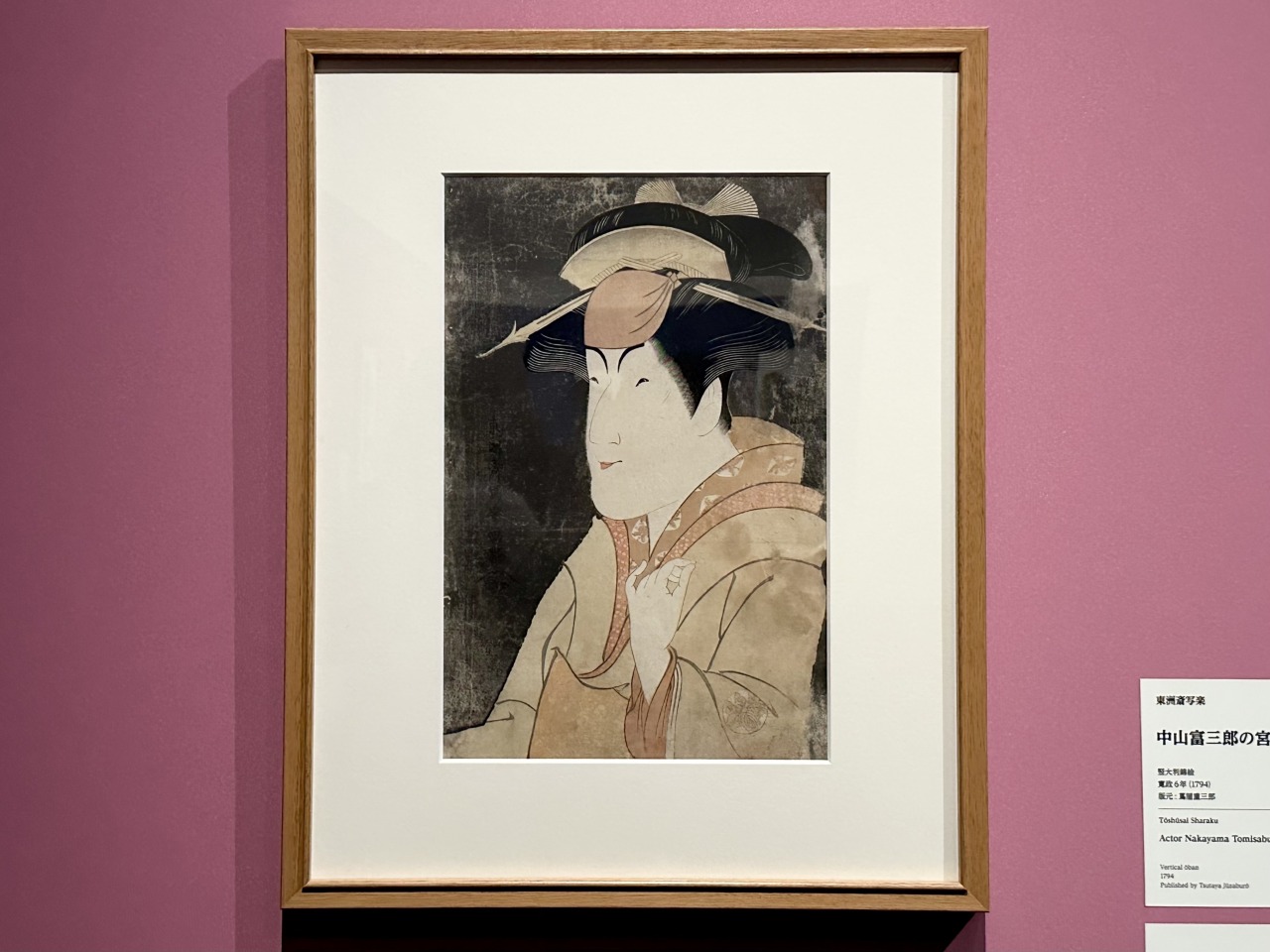
Next up was Toshusai Sharaku , who, like Utamaro, was discovered by Tsutaju and became one of the artists who colored the Golden Age of Ukiyo-e. He produced around 145 nishiki-e prints in the ten months between May 1794 and January of the following year, but then suddenly vanished from the public eye, making him a mysterious figure whose background is largely unknown.
He produced many unique and impactful large-headed portraits of actors, and the period in which he produced them can be divided into four periods according to the performance dates of the plays he covered, allowing for a clear classification of style and specifications. More than half of the Sharaku works on display in this exhibition are large-headed portraits from the particularly popular first period, and it is said to be a very rare opportunity to see so many of his works gathered together in one place.
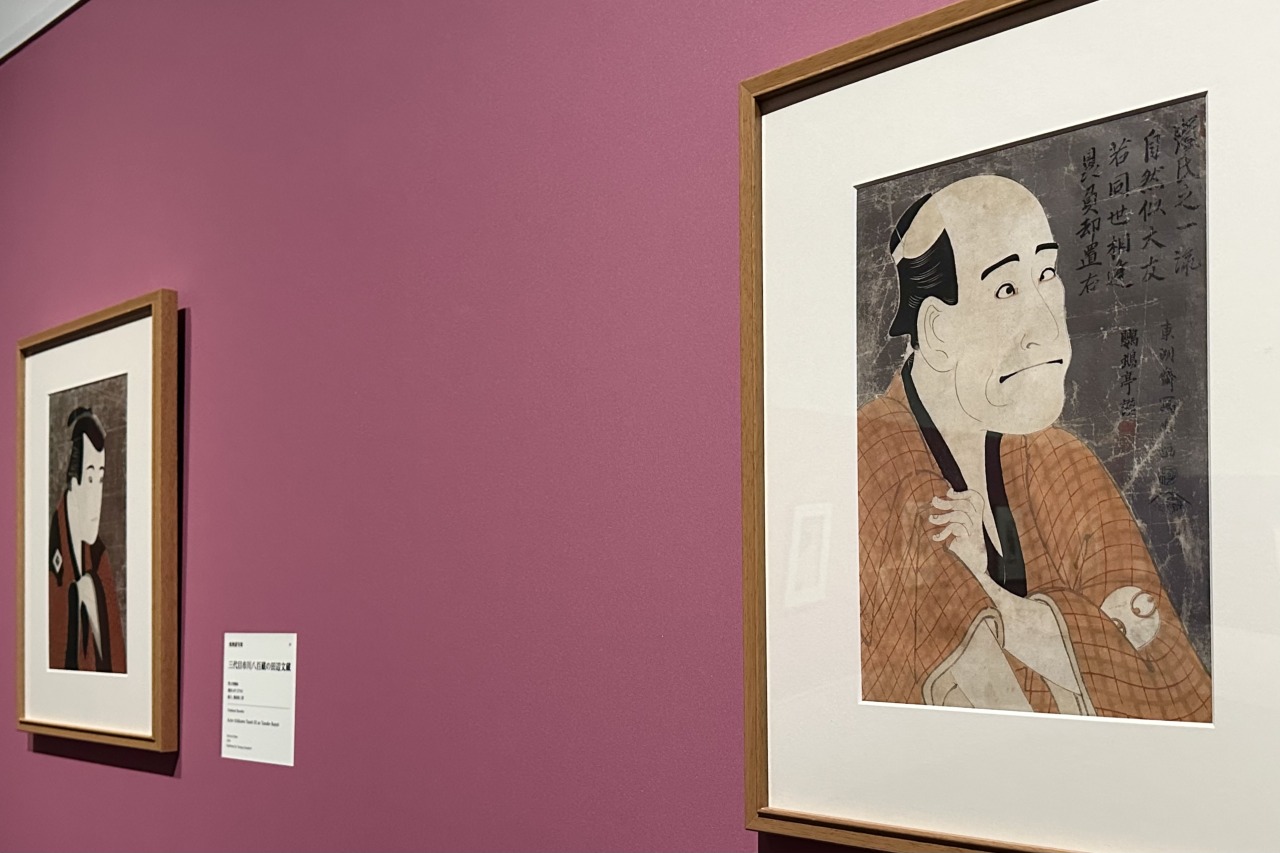

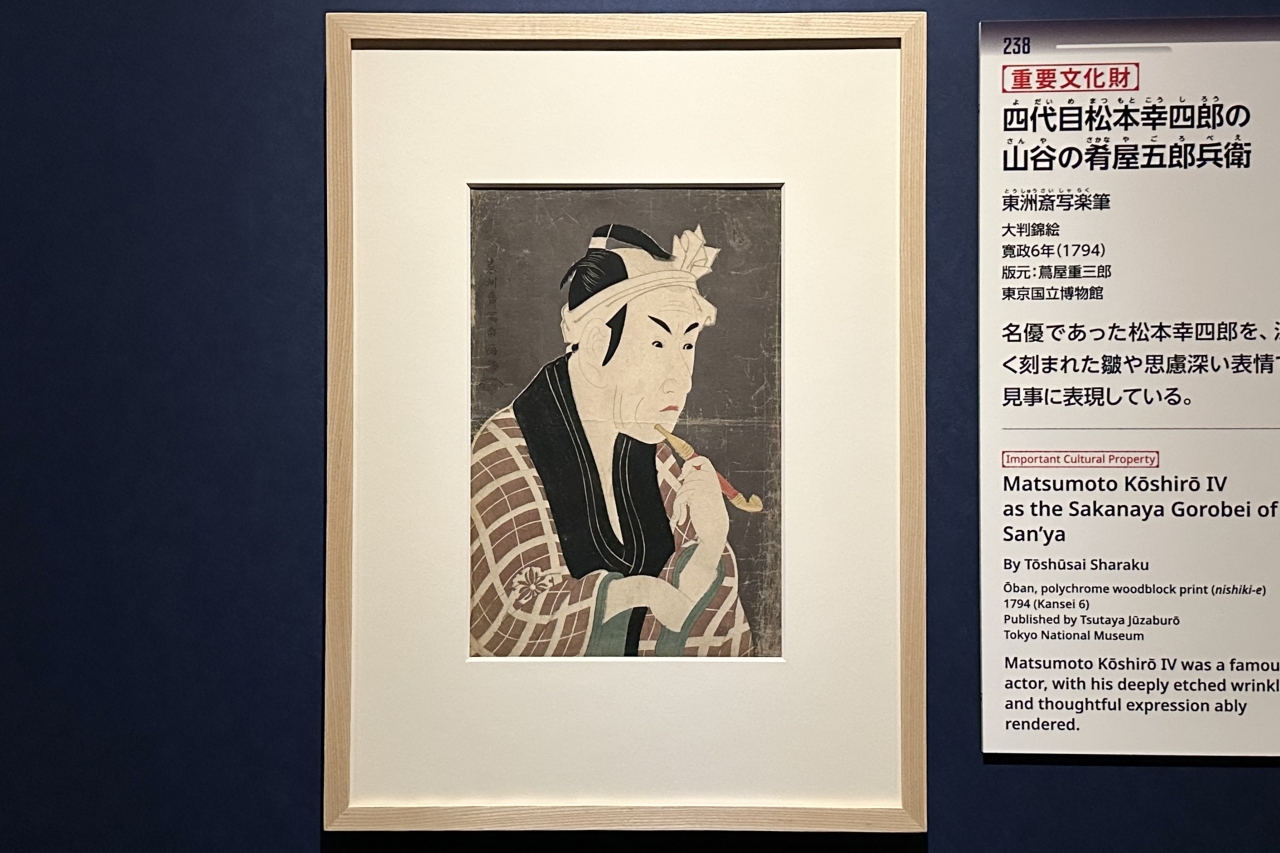
Yamamoto cited "The Second Generation Arashi Ryuzo's Moneylender Ishibe Kanekichi," one of Sharaku's first works, as a clear example of the appeal of his work.
Arashi Ryuzo II was an actor who specialized in playing villains, and in this painting he is playing the role of a moneylender. Noting the actor's unique realistic depictions, achieved through a keen eye for observation, such as the movement of his eyes as he rolls up his sleeves and makes a spectacular pose, the tense movements of each of his fingers, and the wrinkles around his straight mouth, he said, "In an era when there were no zoom cameras or telescopes, it's amazing how much detail he was able to depict. Sharaku was about trying to accurately capture a single moment of an actor's performance."
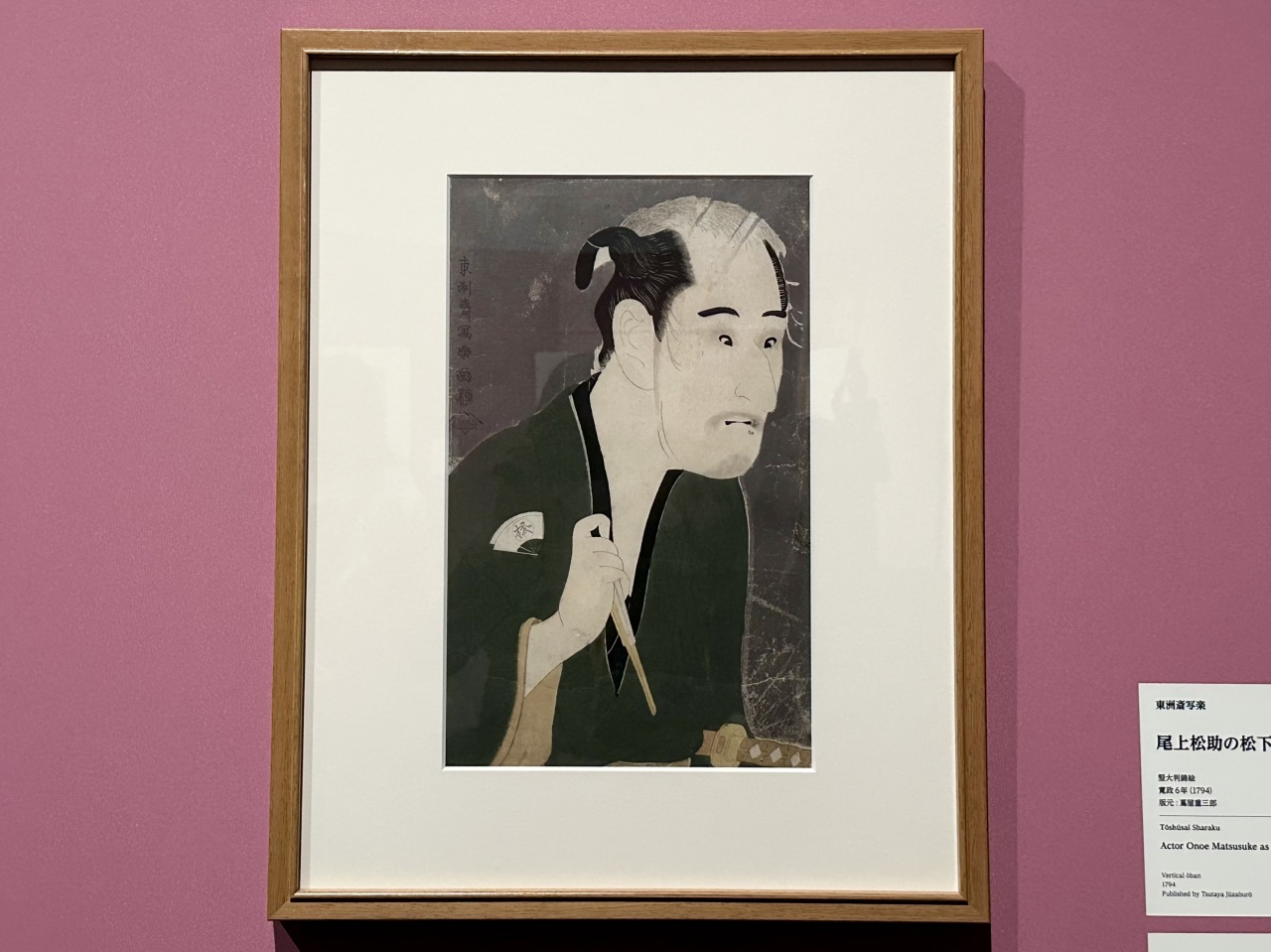

In Onoe Matsusuke's Matsushita Sake Brewery , the depiction of the fallen ronin's long, tousled hair and hollow, sunken eyes stands out. By using dark colors throughout the painting, it is not only possible to express the loneliness of poverty, but also to depict the tragic fate of his imminent death.

At the time, other artists idealized actors, but Sharaku placed emphasis on realism and a sense of presence as if watching the stage up close, rather than on beauty, such as by drawing the masculine bone structure of even female actors. His realistic paintings convey an energy not found in other actor paintings, but his excessive pursuit of authenticity drew criticism from the actors themselves and their fans at the time, and it is said that this was the reason why his career was short-lived.

Chapter 3 "Katsushika Hokusai – Raging Blue"
The third person is Katsushika Hokusai (1760-1849). His name spread throughout Europe during the Japonism movement that occurred in the second half of the 19th century, and he was the only Japanese person to be selected in a recent survey by the American photo magazine LIFE of "The 100 Most Important People in the World Who Have Made the Most Important Achievements in the Last 1,000 Years." It is no exaggeration to say that he is the most famous Japanese painter in the world.

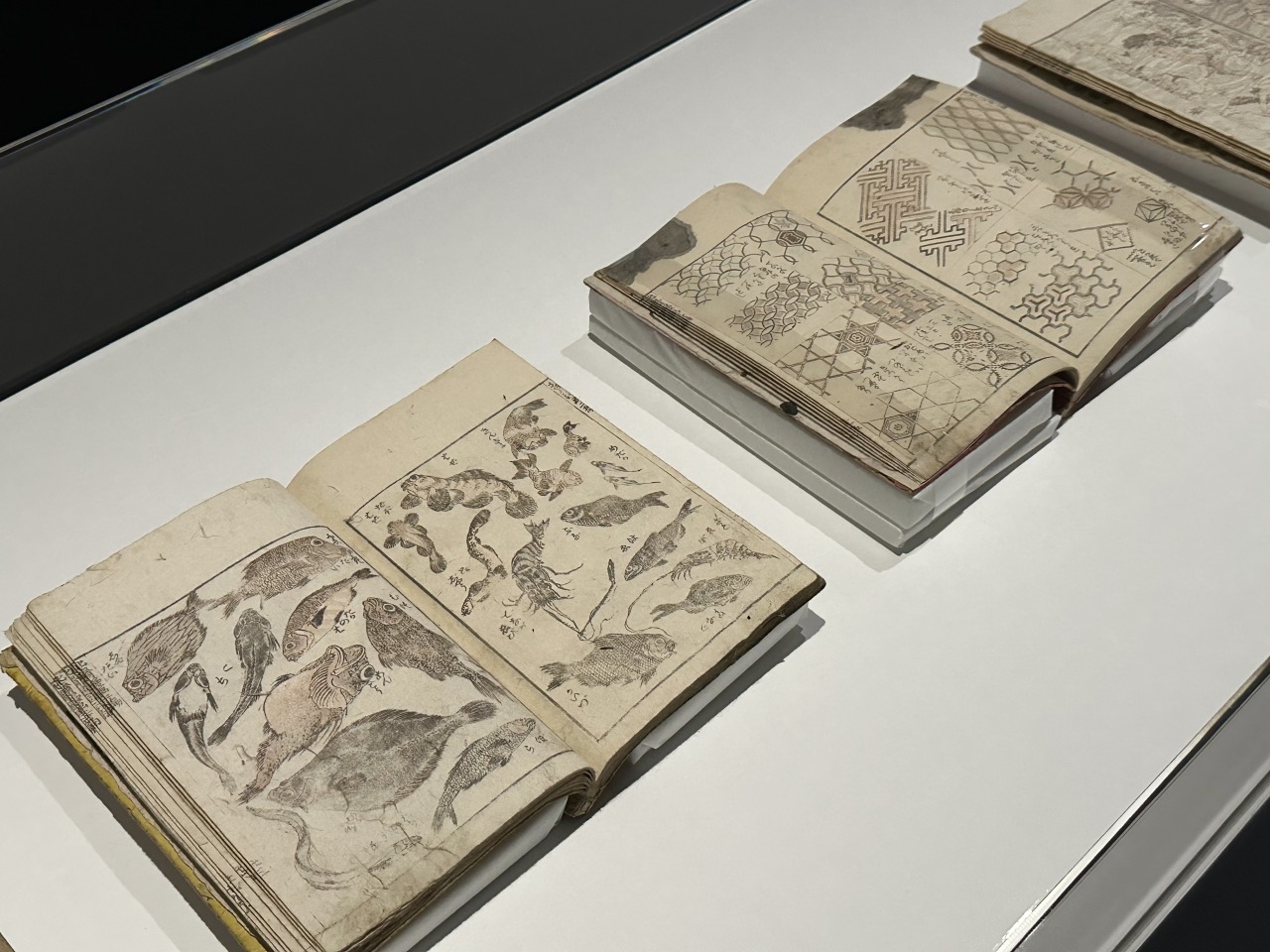
During his 90-year life, Hokusai not only illustrated woodblock prints, but also worked in a wide range of fields, including nishiki-e, surimono prints, and hand-painted illustrations, and continued to paint everything in the universe, not just landscapes, flowers, birds, and people. Just looking at the extraordinary drawing skills of Hokusai's representative picture book , "Hokusai Manga," which is said to contain a total of 4,000 pictures, you can get a sense of the incredible artistic career of a man who devoted himself to painting for over 70 years, eventually calling himself "the crazy artist manji."

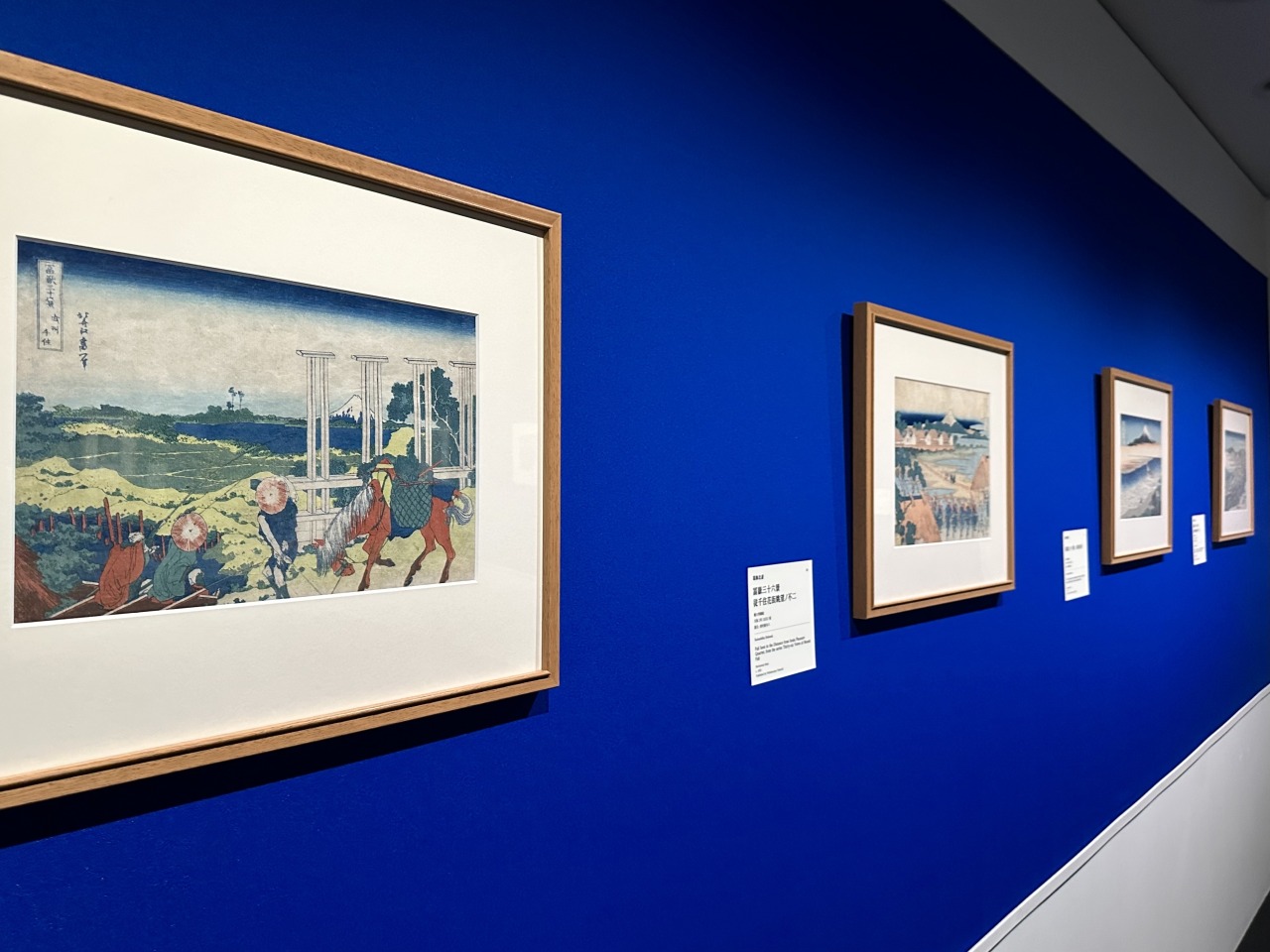
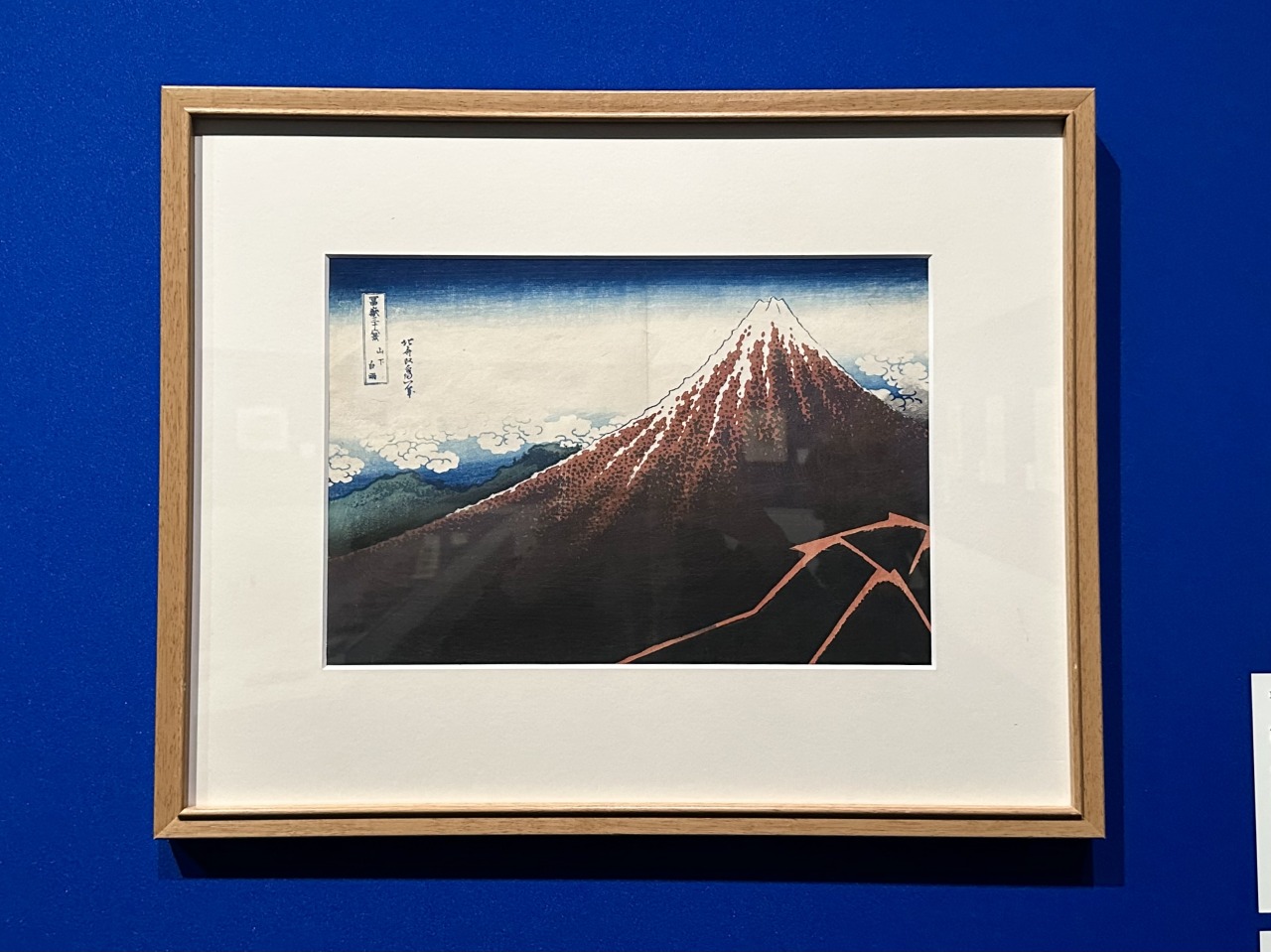
Hokusai was in his 70s when he produced his well-known Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji series, which captures Mount Fuji from various perspectives, but when we look at the works on display from before to after this period, we can see that the colors have become deeper and richer. This is probably due to the change in paint, but these changes, which give us a sense of Hokusai's never-ending spirit of inquiry and ambition, no matter how old he got, are also a highlight.

Among his masterpieces is Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji: Under the Great Wave off Kanagawa , which boldly captures the moment when the spray of waves rises wildly high into the air in the ocean with the shape of Mount Fuji in the distance.
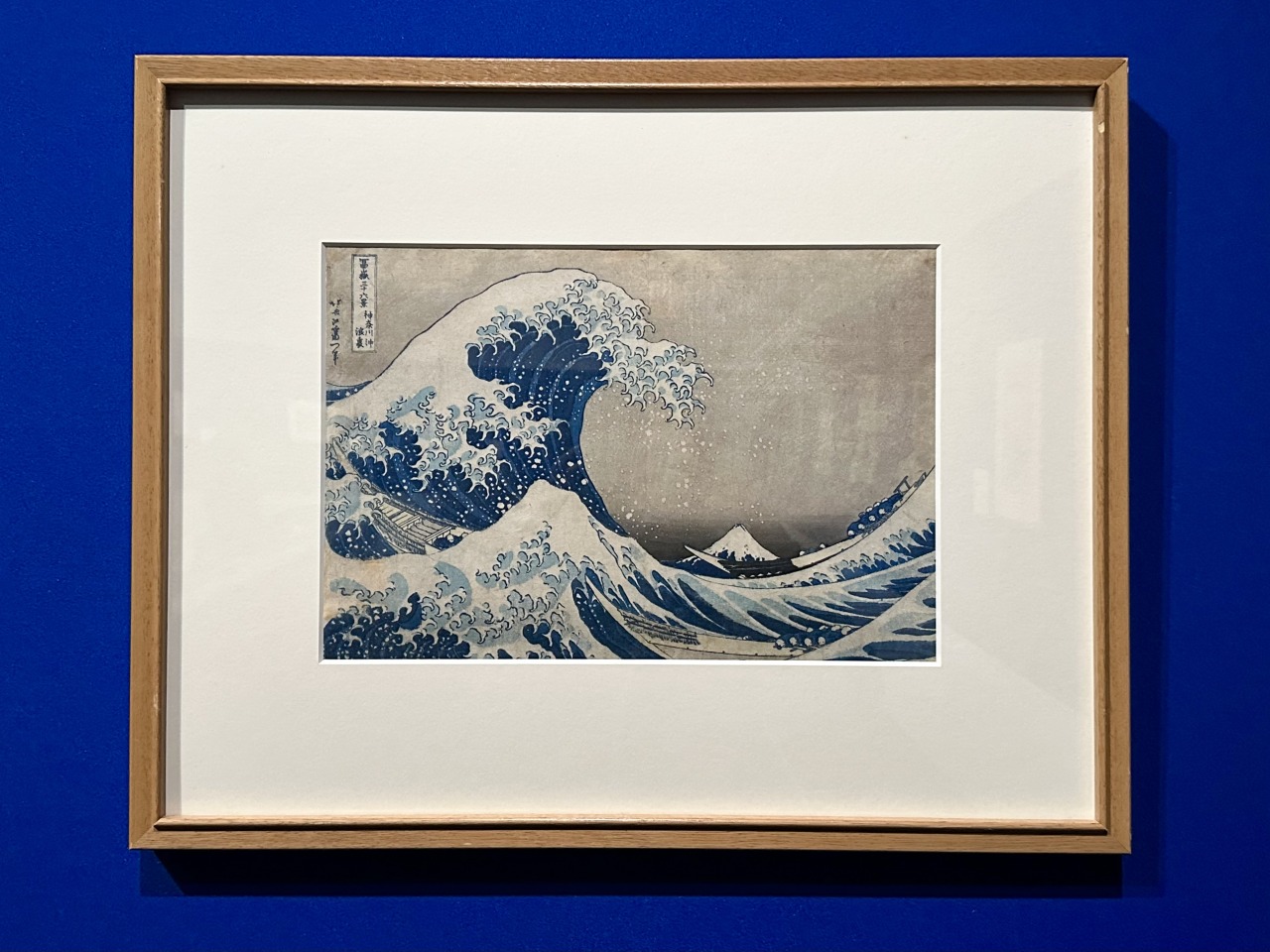

Using this painting as an example, Yamamoto pointed out that one of the attractions of Hokusai's work is the "visual tricks."
"It has been pointed out that Hokusai purposely included designs in his works that would guide the viewer's gaze. When people look at this painting, I think their eyes are first drawn to the violently rising waves. The waves in the foreground are triangular, and on closer inspection they correspond to Mount Fuji in the distance. The painting is designed to naturally guide the viewer's gaze from the triangle in the foreground to the triangle in the distance."

Similarly, the intention to guide the viewer's eye is clear in Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji, Sazaido Hall of the Gohyakurakan Temple , where various lines from the floorboards, roof, and balustrade of the hall, to the fingertips of the worshippers, converge on Mount Fuji towering in the background. Hokusai, who excelled in Western perspective drawing, also excelled in this work, demonstrating his skill with geometric composition.
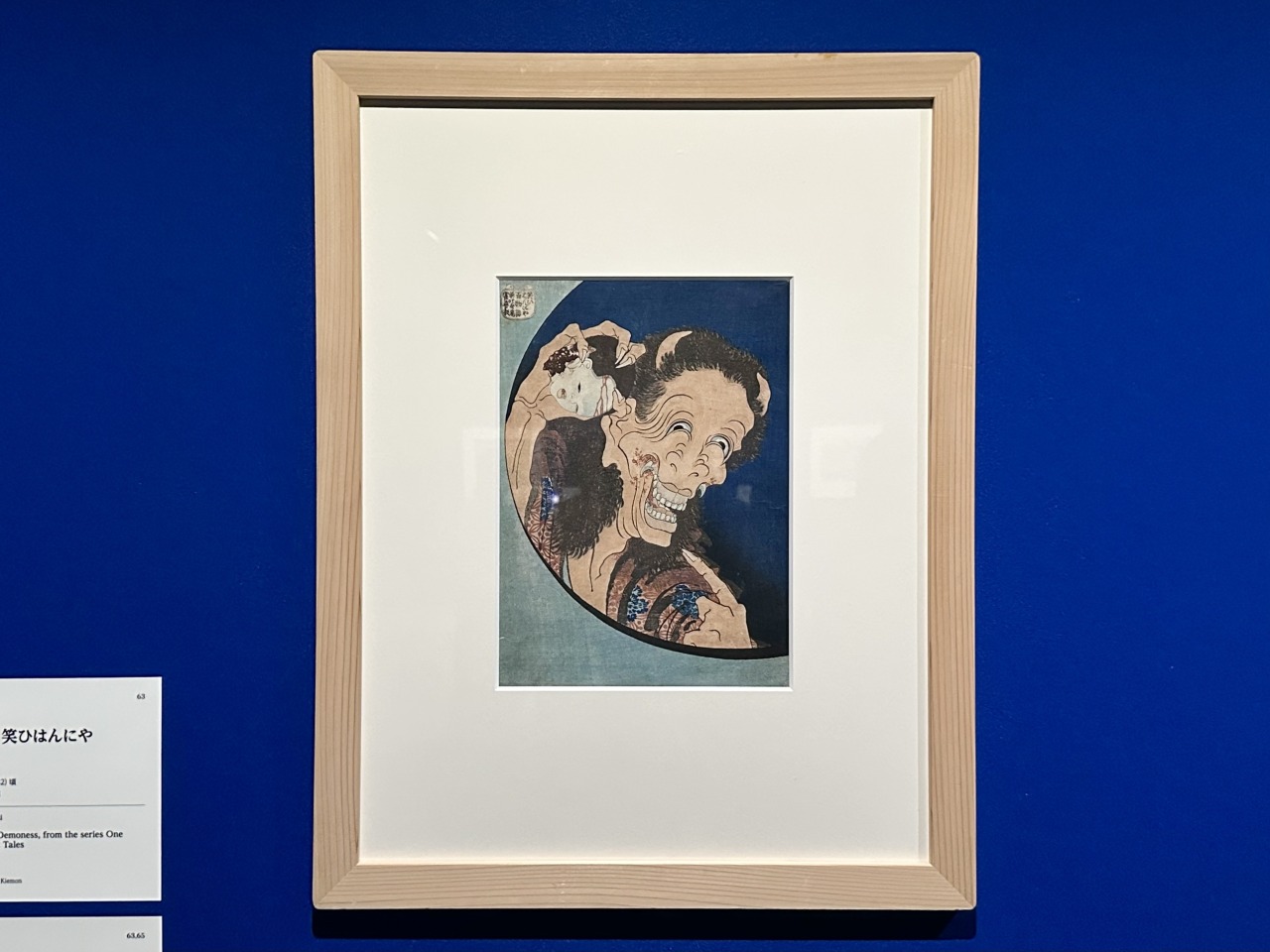


Chapter 4: Utagawa Hiroshige – Edo in Rain, Moon and Snow
The next artist, Utagawa Hiroshige (1797-1858), initially produced portraits of beautiful women and actors, but his breakthrough series , "Fifty-three Stations of the Tokaido," firmly established him as a landscape painter.
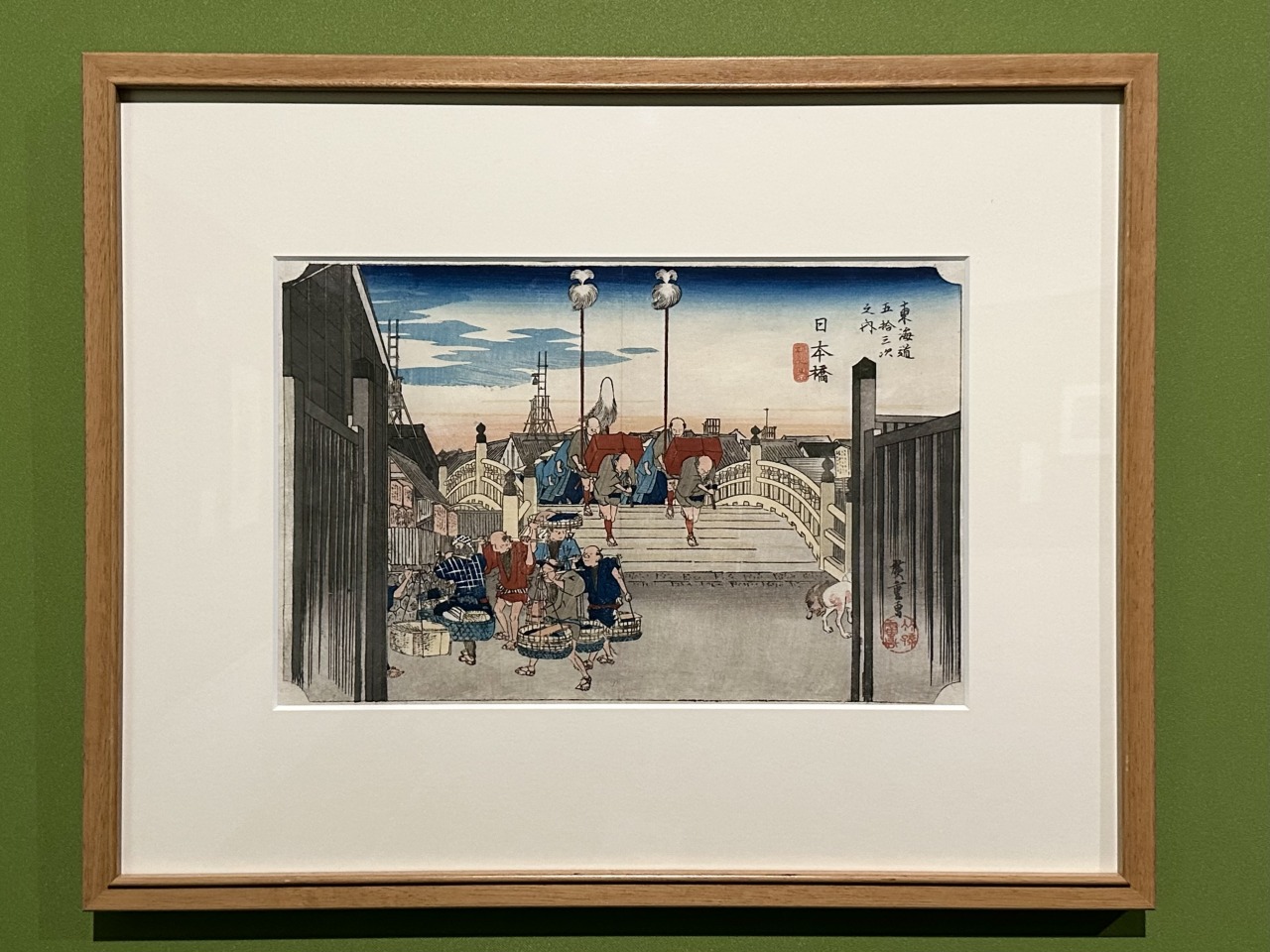

The series depicts 55 landscapes, including the 53 post towns along the Tokaido road connecting Edo and Kamigata, as well as Nihonbashi and Kyoto's Sanjo Ohashi bridge. It became an explosive hit, fueled by the travel boom caused by Jippensha Ikku's "Tokaido Chu Hizakurige." It is also noteworthy that it was published at roughly the same time as Hokusai's "Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji" series, which is often compared to Hokusai's masterful landscape painting.
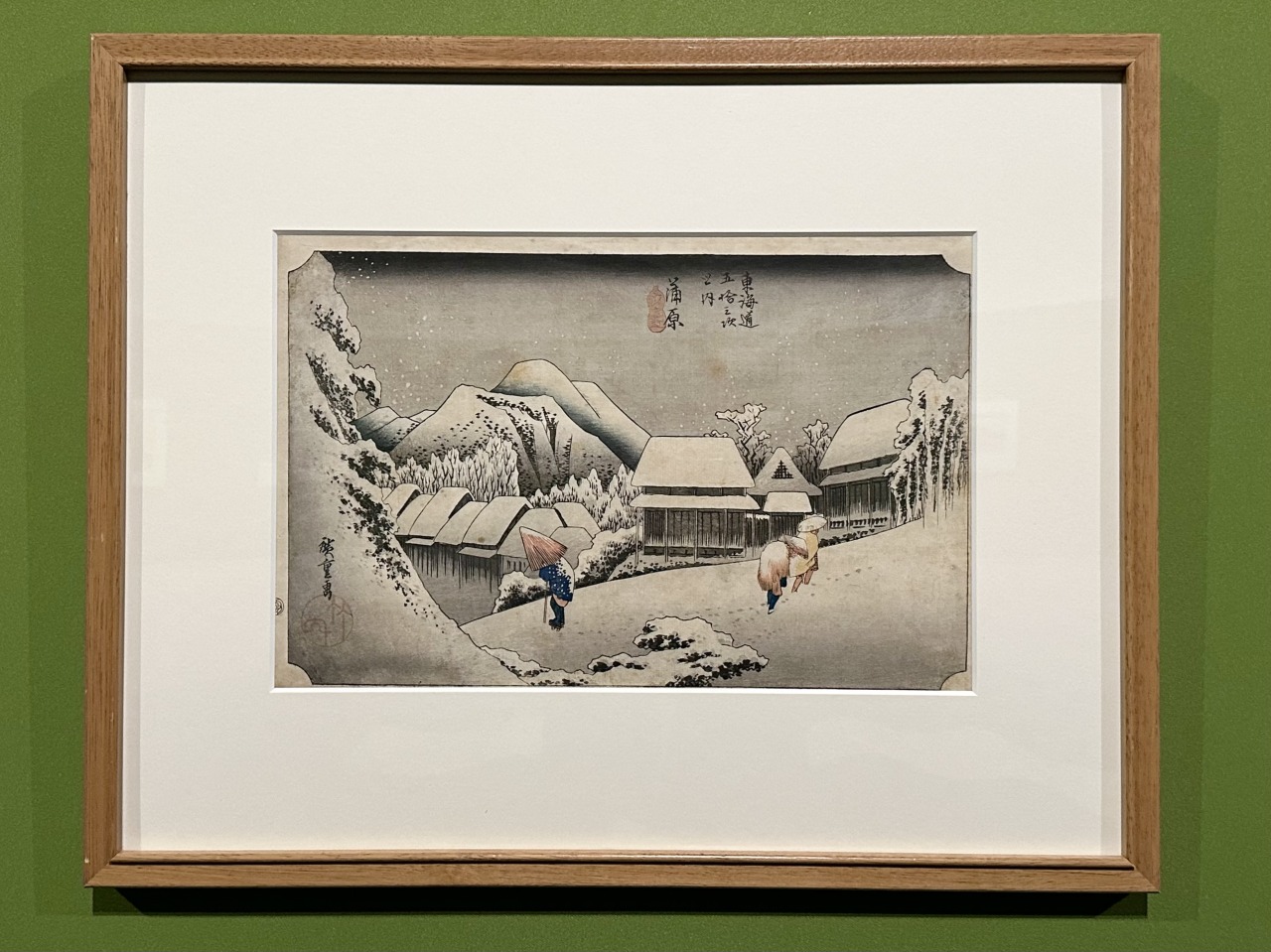

Regarding Hiroshige's landscape paintings, Yamamoto says the following:
"Although they are landscape paintings, they also depict local people, travelers, the customs and customs of travel, and the atmosphere, which creates a sense of charm. They are not just landscape paintings, nor are they just portraits, nor are they just nature, nor are they just people's lives. The beauty of Hiroshige's works is that they are all integrated together."
Both Hiroshige and Hokusai are said to have been avid travelers. Hiroshige made full use of the natural scenery, the climate, and the people who lived there, while Hokusai boldly exaggerated the formative qualities of the things he saw. It is interesting to compare the differences in their perspectives and directions.
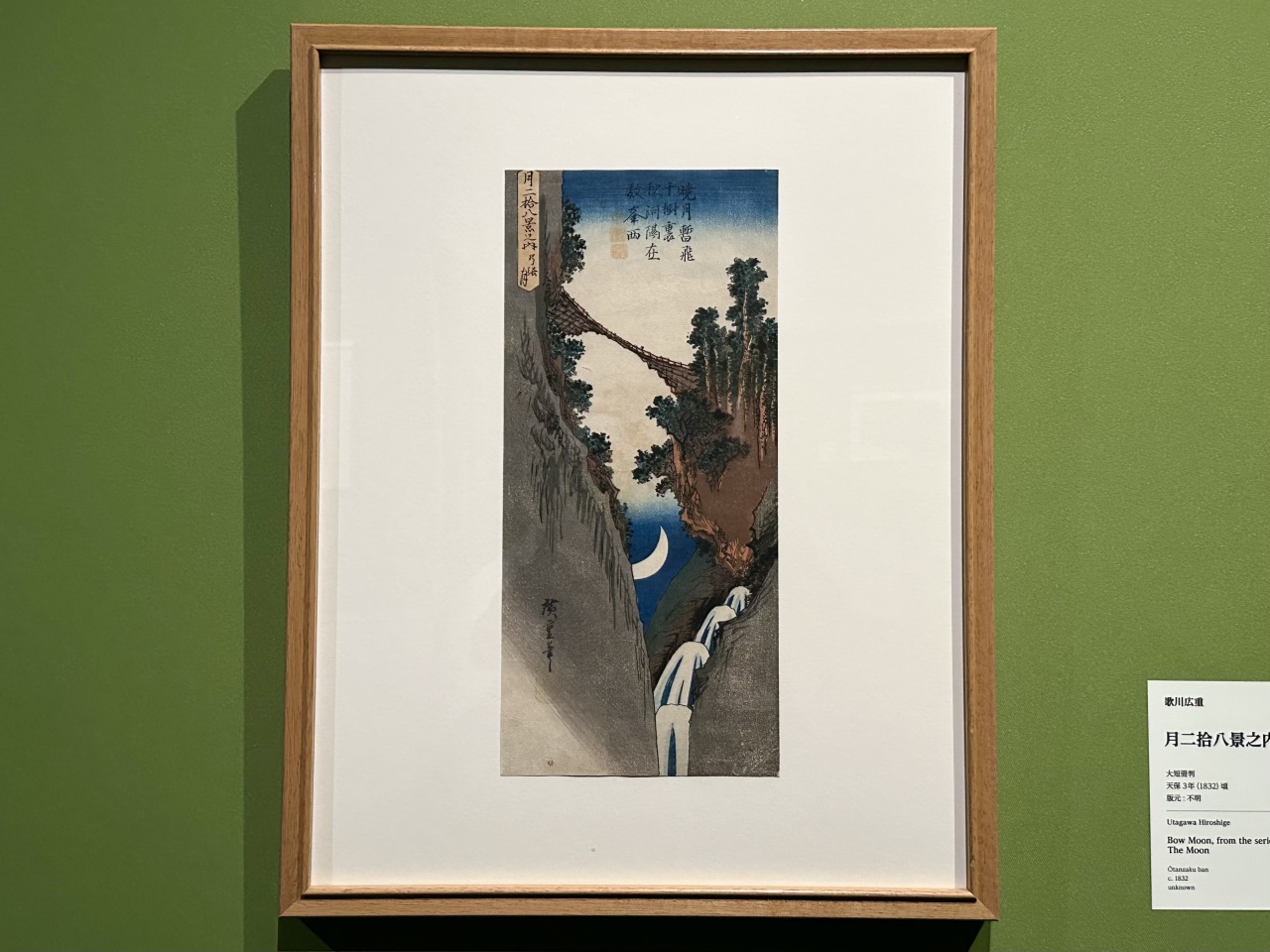
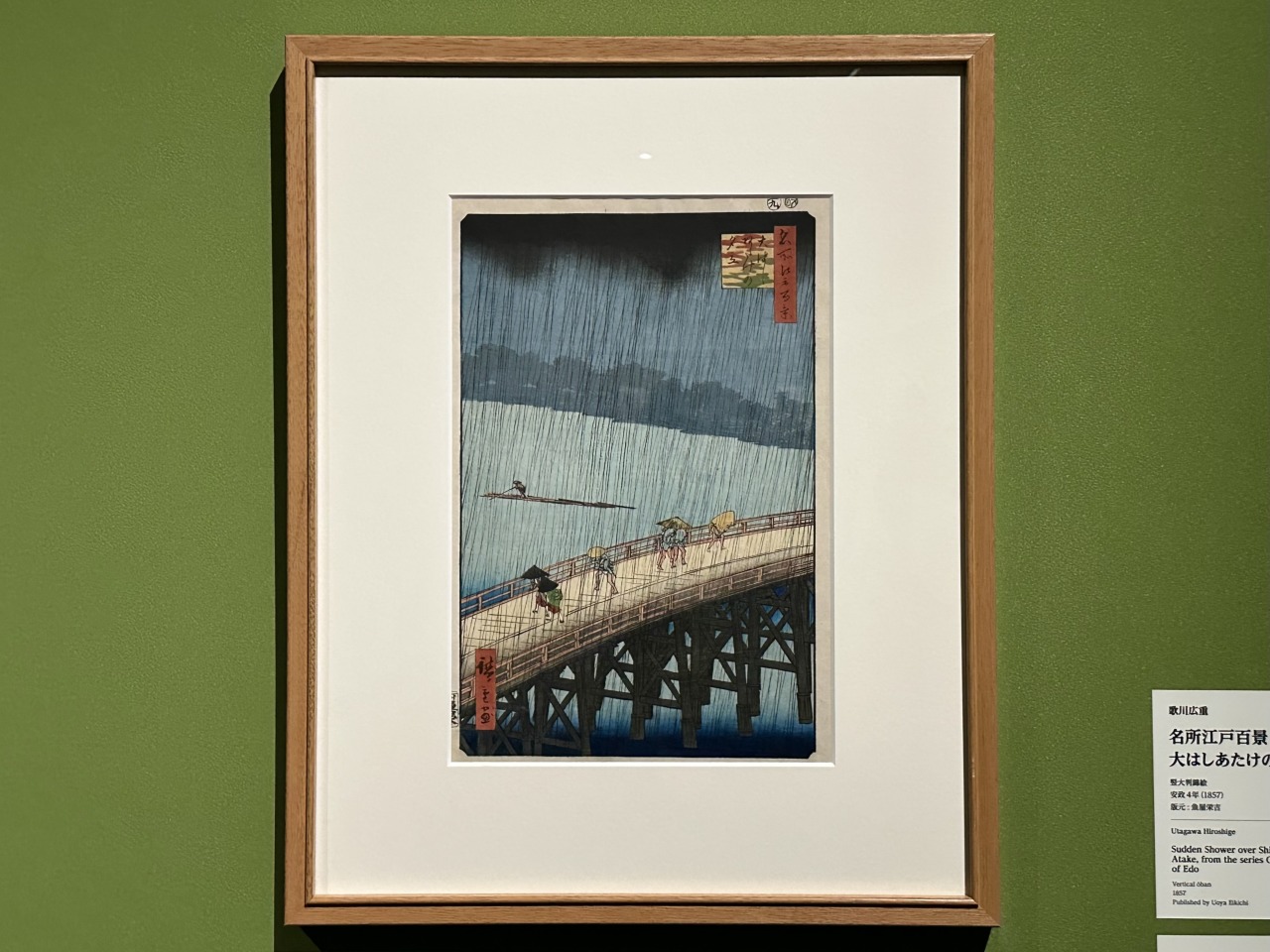


Hiroshige was also skilled at painting famous places around Japan, and in his "One Hundred Famous Views of Edo" series, a masterpiece from his later years, he even attempted the unusual vertical layout of a landscape painting.
Particularly striking is "One Hundred Famous Views of Edo: The Plum Tree Shop at Kameido," in which the plum tree branches are drawn extremely enlarged in the foreground, and the overall view of the plum tree house is captured in the gaps between them, creating a sufficient sense of perspective even in a vertical frame. This type of composition is called a close-up composition, and was a favorite of Hiroshige in his later years.

One of the great features of Hiroshige's work is the way he varies the composition of each work, from taking the same perspective as the traveller, to looking down from a great height like a bird, to deliberately placing the rugged rock face in the center of the picture to express the precipitousness of the cliffs. The unrestrained spatial expression, drawn with imagination as if it were taken by drone, never tires the viewer.
Chapter 5: Utagawa Kuniyoshi – Heroes and Spectacles
Chapter 5 features Utagawa Kuniyoshi (1797-1861), who was the same age as Utagawa Hiroshige and was active during the late Edo and Meiji periods. The atmosphere of the exhibited works has changed drastically from previous exhibitions, presenting a spectacular, action-packed drama.
Kuniyoshi made his breakthrough with the "Popular Suikoden" series, which combines dynamic character portrayals and beautiful colors in dynamic scenes created with bold brushwork. He created many Japanese heroes and heroines, and broke new ground with his fantastical and exciting warrior paintings and rebellious and humorous caricatures.
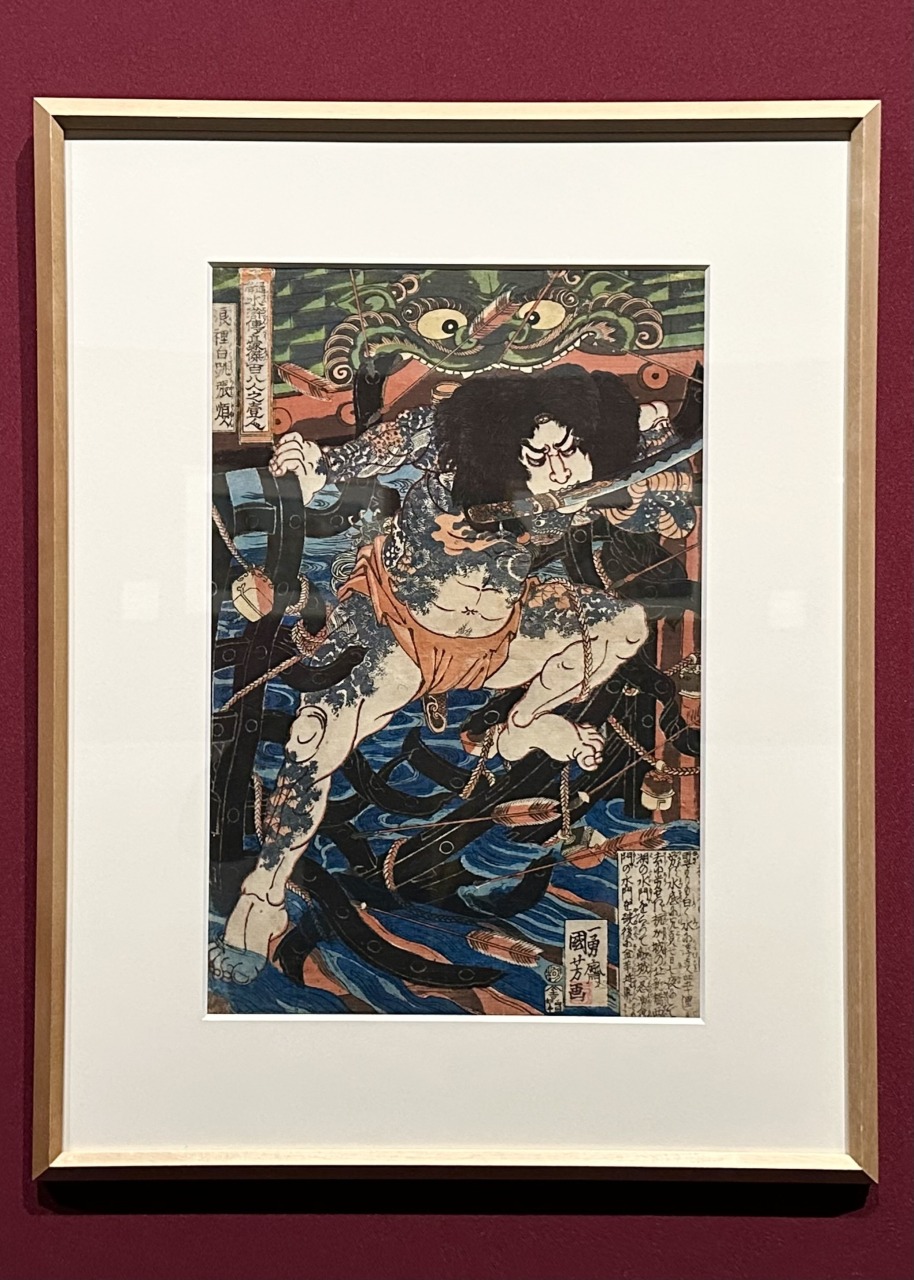

One of the 108 Heroes of the Popular Suikoden: Zhang Shun Leaps White on the Rise is renowned as a masterpiece in the series, depicting the scene in which Zhang Shun, the leader of the navy, falls into an enemy trap, is hit by countless arrows and meets a heroic end. The depiction of his glaring expression and each strand of standing hair conveys the menace of someone prepared to die.
As in this work, Kuniyoshi often decorated his characters with flashy tattoos (irezumi), and it is said that these were so impressive that they sparked a tattoo boom in Edo.

The Old Palace of Soma, with its striking giant skull straddling the seam of the paper, is a work based on Santo Kyoden's Yomihon (a long illustrated novel that was popular in the Edo period). The distinctive widescreen triptych (a composition that treats a series of works as one large screen) is a technique that Kuniyoshi was good at.
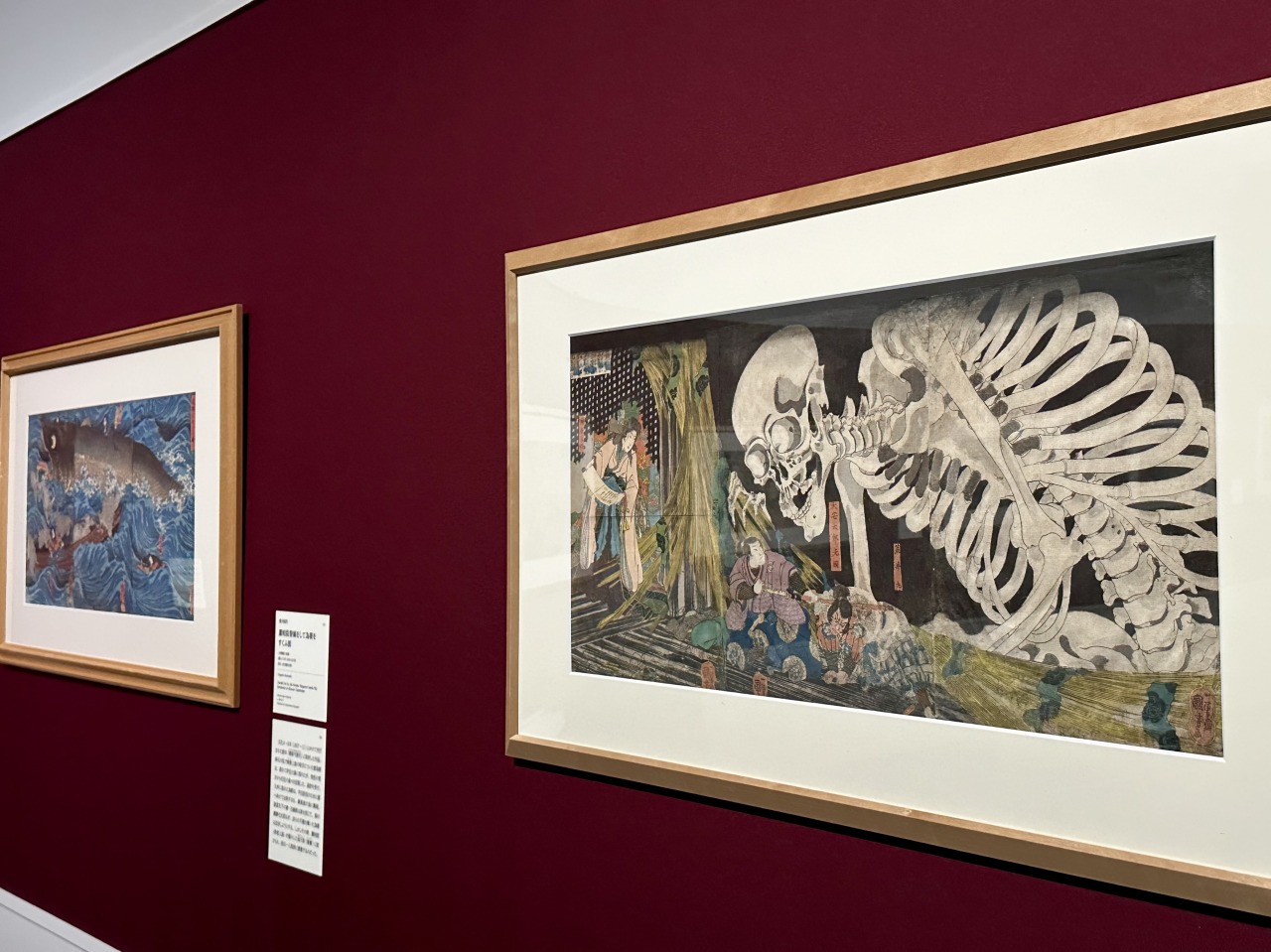

The painting depicts the appearance of strange creatures in the ruins of Taira no Masakado's Imperial Palace, but in the illustration in the book, which shows countless small skulls, Kuniyoshi has uniquely changed it to a single giant skull. Furthermore, the powerful effect of the triptych shows a glimpse of Kuniyoshi's unique creativity.
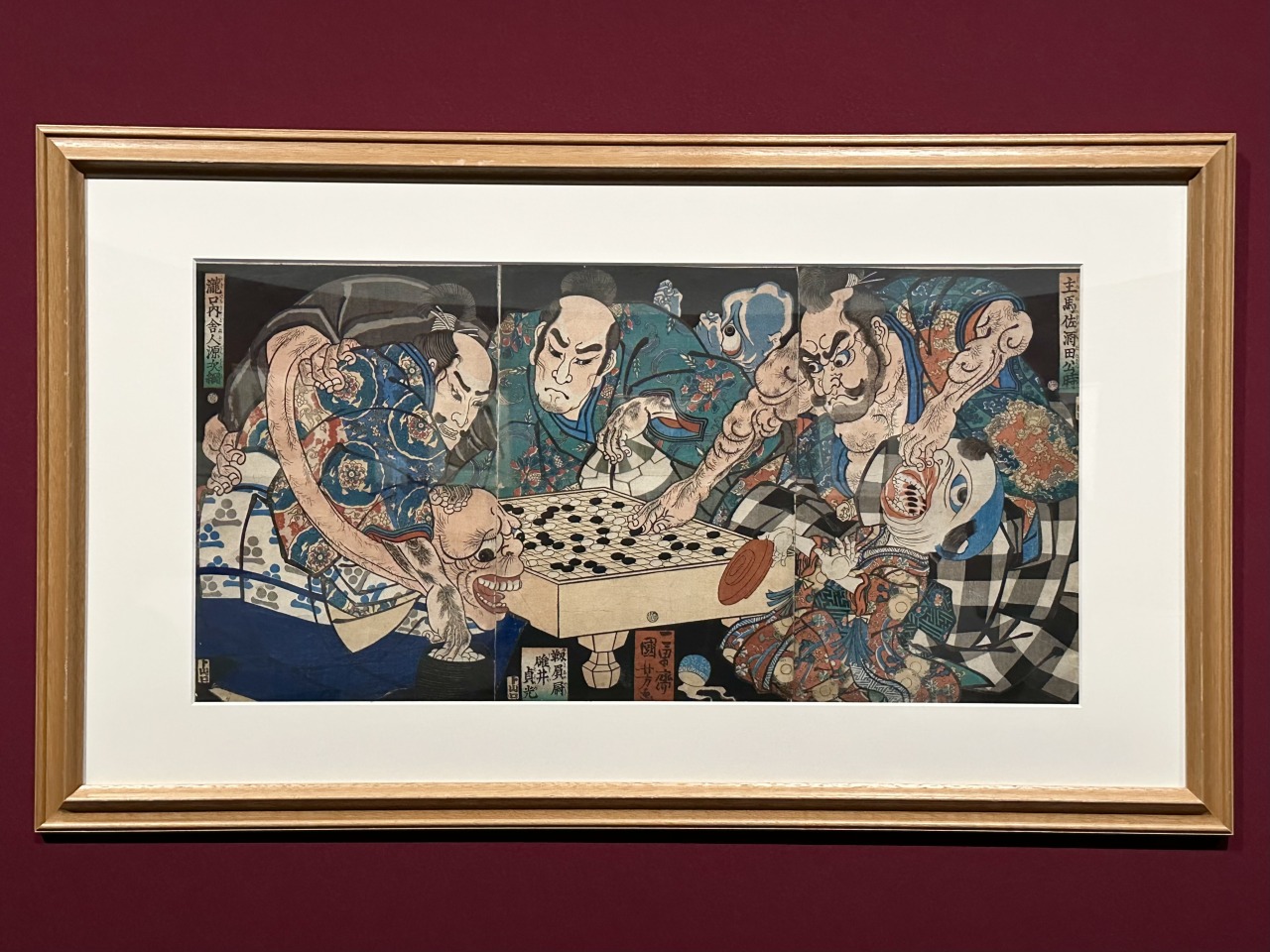

Although Kuniyoshi excels at depicting action-packed warriors, he does not always depict spectacular scenes. For example, "Sakata Kintoki, Usui Sadamitsu, Minamoto no Tsugutsuna and Monsters" depicts the scene where Minamoto no Yorimitsu's four heavenly kings are playing a game of Go with monsters plotting evil deeds. The humorous contrast between the pitiful monsters who are easily subdued and the samurai who are playing Go with stern but unaffected expressions will make you chuckle.
Honor: Invincible to the Right, Jingoro to the Left depicts the famous Edo sculptor Jingoro and the sculptures that surround him. However, the scattered trademarks of Kuniyoshi, such as the Hell Transformation Picture Dotera, the Hoto Seal cushion, and the cat that is beside him, show that in fact it is Kuniyoshi himself who appears in the work, likening him to Jingoro.
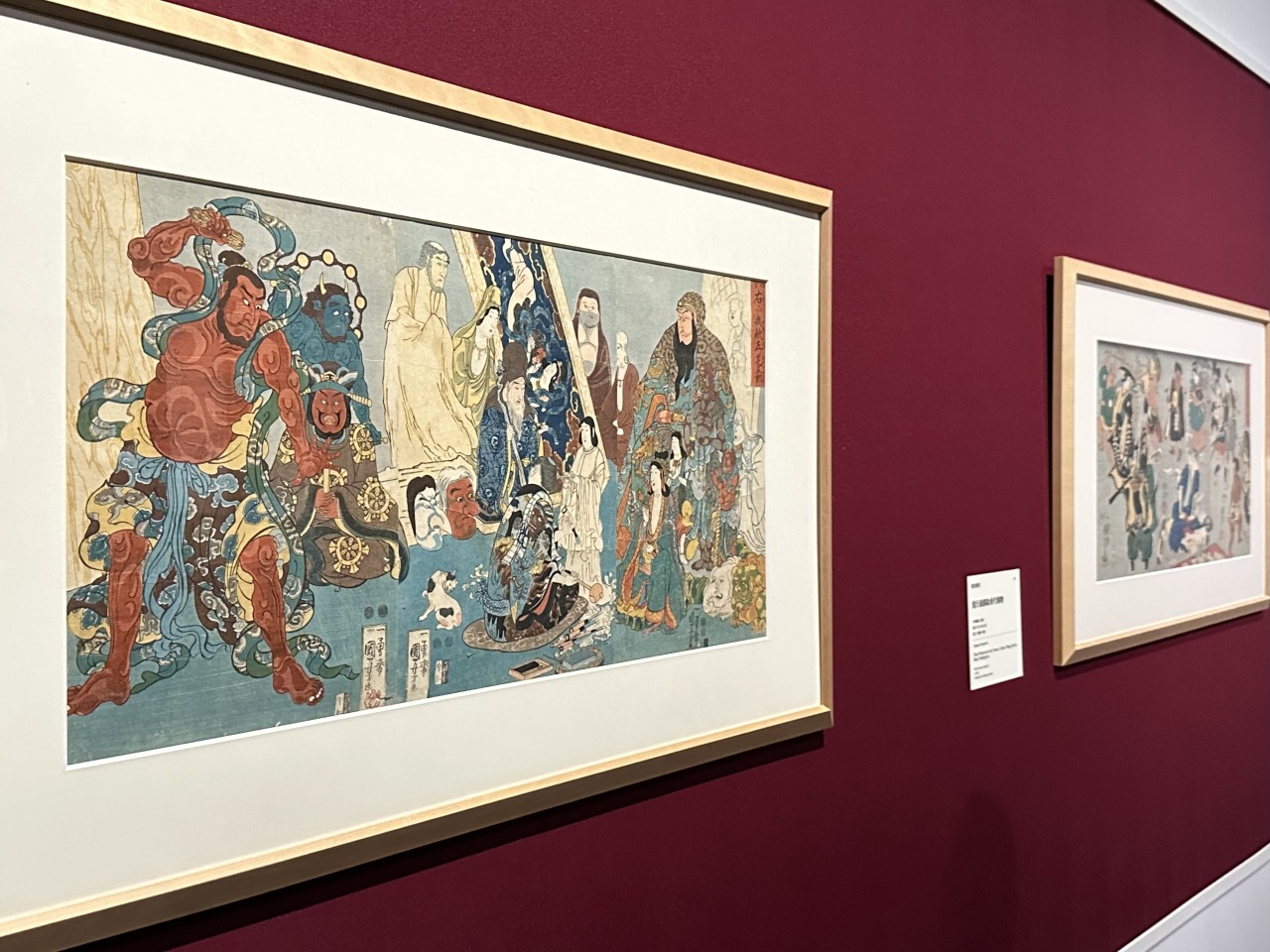

Yamamoto also points out that the faces of the surrounding sculptures, such as Nio and Guan Yu, are caricatures of actors.
"During the Tenpo Reforms, the entertainment industry was cracked down on and ukiyo-e artists were banned from painting pictures of actors or beautiful women. But the artists continued to create works by any means possible, and Kuniyoshi in particular had an extremely rebellious spirit, so even after the reforms relaxed, he continued to paint Buddhist statues resembling actors, as if to mock the shogunate, and demonstrate what he was capable of. He was a commoner who painted pictures for the common people, yet he rebelled against authority in this way. That was the artist Kuniyoshi."
The "Five Great Ukiyo-e Artists – Utamaro, Sharaku, Hokusai, Hiroshige, Kuniyoshi" exhibition will run until Sunday, July 6, 2025. One of the exhibition's catchphrases is "Find your favorite!" Even if you are not familiar with ukiyo-e, we encourage you to experience the masterpieces of the five great stars who reached the pinnacle of ukiyo-e at this exhibition and find your favorite artist.
Overview of the "Five Great Ukiyo-e Artists Exhibition – Utamaro, Sharaku, Hokusai, Hiroshige, Kuniyoshi"
| Dates | May 27th (Tue) – July 6th (Sun), 2025 *No closing days |
| Opening hours | 10:00-17:00 (Last admission 30 minutes before closing) |
| venue | Ueno Royal Museum (1-2 Ueno Park, Taito-ku, Tokyo 110-0007) |
| ticket | Please visit the official website for details. |
| Organizer | Ueno Royal Museum / Fuji Television Network |
| inquiry | 050-5541-8600 (Hello Dial, all day/9:00-20:00) |
| Exhibition official website | https://www.5ukiyoeshi.jp/ |
*The contents of this article are current as of the time of coverage. Please check the official exhibition website for the latest information.
Article provided by: Kokosil Ueno